Smart Window for Efficient Light and Heat Control
The global expansion of the economy and population has spurred a surge in energy requirements. As per research conducted in 2018, within European Union households, space heating accounts for a significant 63.6% of the overall energy consumption, while space cooling via air conditioners and electric fans contributes to 20% of the world's current electricity consumption.
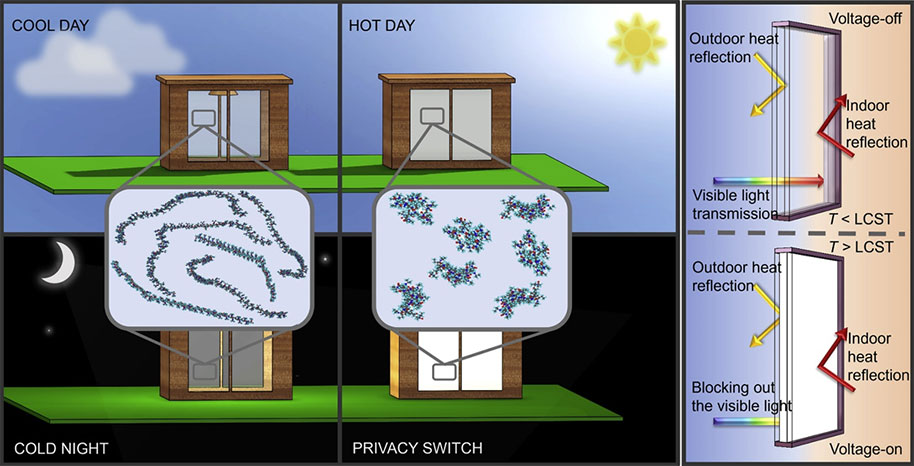
A notable area of inefficiency in building design lies in windows, where energy leakage remains notably high. Scientists have been working on developing a type of window that can help regulate the amount of heat that enters or leaves a building, called smart windows. For this purpose, research has advanced toward smart window technologies centered around electrochromic, photochromic, and thermochromic materials. These materials enable users to adjust the window's transparency through voltage application, changes in light intensity, and temperature variations. The thermochromic smart window stands out among these technologies due to its affordability, passive control features, and effective temperature management. However, many of these studies have focused on adjusting the amount of visible light that comes in during the day, and don't consider privacy at night when temperatures drop.
Sabanci University Nanotechnology Research and Application Center researchers have developed a new kind of smart window that allows people to control how much light comes in and out, using a special material that can change from transparent to opaque when it reaches a certain temperature. It uses a special coating made of very thin layers of metal and oxide, as well as a temperature-sensitive layer, to make this possible. The window can automatically darken in hot weather, or it can be darkened manually with a small amount of electricity. The coating on the window also helps to reduce energy use for heating and cooling by blocking some of the heat that comes in from the sun. Overall, this new smart window has many useful features that can make buildings more energy-efficient and comfortable.
Mitmit, C., Mocan, M., Camic, B. T., Cingil, H. E., & Tan, E. M. (2023). Broadband light and heat management with a self-regulating and user-controlled thermochromic smart window. Cell Reports Physical Science, 4(1).
Ref: Broadband light and heat management with a self-regulating and user-controlled thermochromic smart window
SUNUM Scientific Committee:
Aysun Altan
Feray Bakan Mısırlıoğlu
Nokta Çelik
Authors:
Ceren Mitmit
Merve Mocan
B. Tugba Camic
Hande E. Cingil
Eric M.M. Tan
 New generation Osteoarthritis Treatment: Microneedle Arrays for Regeneration and More
New generation Osteoarthritis Treatment: Microneedle Arrays for Regeneration and More MXene: A Rising Star 2D Material
MXene: A Rising Star 2D Material Smart Window for Efficient Light and Heat Control
Smart Window for Efficient Light and Heat Control
- 2D Materials
- Agriculture
- Agrochemicals
- Ammonia Gas
- Biomaterials
- Biomedical Applications
- Borophene Focused Ion Beam
- Carbon Nanotube
- Carbon-Based Nanomaterials
- Clean Room
- Coating
- Display Technologies
- DNA Technologies
- EMI Shielding
- Energy Storage
- Energy Technologies
- Fire Retardancy
- Gas Sensor
- Graphene
- Graphene-Based Materials
- Heat Control
- Light Control
- Lithium-ion Batteries
- Metal Nanoparticles
- MXene
- Nanofabrication
- Nanomaterials
- Nanoparticle-Based Gene Carriers
- Nanotechnological Sensors
- Nanotechnology
- Personal Electronics
- Quantum Dots
- Selective Breeding
- Smart Clothing
- Smart Window
- Stretchable Batteries
- Sustainable Crop Production
- Targeted Crop
- Thermochromic
- Transition Metal Carbides
- Transition Metal Carbonitrides
- Transition Metal Nitrides
- Wearable Electronics


